Let's Talk
Request a private consultation. Discover how you can Make Your Move™.
There is really no excuse for 'I Didn't Know' or 'That Was Unforseen'.
The giveaway guide to navigate a financial model quickly. No matter how complex.
DownloadFinancial modelling is the work undertaken to build a financial model. A financial model represents management’s outlook for a real-world financial situation. It is a mathematical model constructed to summarize the performance of a business, project, or any other investment. Financial models are often used a variety of strategic decisions as summarized in the exhibit below.
exhibit 1: uses of financial models

The use of various input parameters helps a business see likely financial outcomes of a business decision in quantitative terms before committing funds or resources. The model may also summarize events for the end user and provide directions regarding possible actions or alternatives.
To build a financial model, one needs skills include knowledge of operations, budgeting, accounting, valuation and spreadsheet programming.
A financial model takes in parameters like operational metrics, market metrics (e.g. inflation), timing, revenues, expenses, capital and operating expenditures, etc. The model tests how changes in one or more input assumptions affects outputs like cash flow, return on investment and payback period. This allows leaders to quantify a business decision, decide what resources, stakeholders and policies to engage to support a project. The financial model also highlights future financial obligations the business must meet and describes expectations from investors and lenders.
Large scale financial models can be time-consuming to build and daunting to operate. Building a simple to understand, responsive and flexible financial model often requires specialized expertise.
A large business may use third-party software to perform financial modelling, analysis and documentation. Such systems may not be fit for purpose if the business requires a level of customization or flexibility beyond what the software can offer. In-house accountants may also not have the blend of expertise and experience to code a bespoke financial model with data analytics and visualization options.
The top 5 financial models and their applications are as follows:
Three Statement Model
A three-statement model is a commonly requested starting point for financial modelling. It connects three key financial statements, i.e. the income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements using formulas. It is set up to ensure that a set of assumptions can drive changes in the model as an entire set. The linking of all three statements requires strong accounting and finance expertise. It is also not enough to have textbook knowledge. Coding models that can operate smoothly under a range of input assumptions, are able to calculate and return outputs speedily, and takes up a small file footprint requires many hours of hands-on practice to deliver a high-quality user experience.
exhibit 2: profit & loss statement
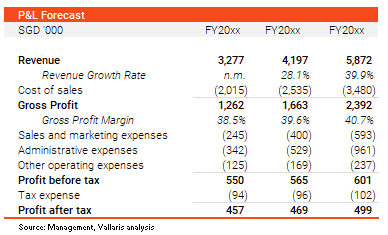
The income statement is the most analyzed of the three statements. It reveals a firm’s ability to generate profit but does not show balance sheet movements required to produce cash flow. Hence, it may not be sufficient to solely rely on income statement to give a full picture of the firm’s financial outlook. If you have ever wondered why your profitable business is gasping for air to meet payments, e.g. pay employees, salaries and loans, just know that profit is not cash flow. It is cash flow that will help you manage your business as a going concern.
exhibit 3: balance sheet
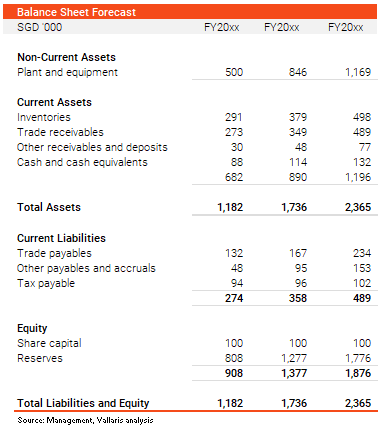
It is useful for the income statement to be paired with a balance sheet as it represents assets in place. A balance sheet forecast can also explain investments in assets required to support operations and future growth.
The cash flow statement presents the changes in cash inflow and outflows within the firm. It explains movements of cash related to operations, investment and financing.
The three statement model prepares a dynamically connected one single financial model which is used as the base of complex financial models like leverage buyout, discounted cash flow, mergers & acquisitions, initial public offering, leveraged buyout and other financial models which we are about to explore next.
Discounted Cash Flow (“DCF”) Model
The three-statement model sets the foundation for the DCF model to build on. The purpose of a DCF model to to calculate the net present value of a business. It discounts a stream of future cash flows into one lump sum payment in today’s dollars.
The cash flow information is extracted from the three-statement model. DCF analysis is an intrinsic value approach to forecast the firm’s unlevered free cash flow. Adjustments are made on the cash flow information where necessary, and then discount back to today at the firm’s Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC).
exhibit 4: discounted cash flow model
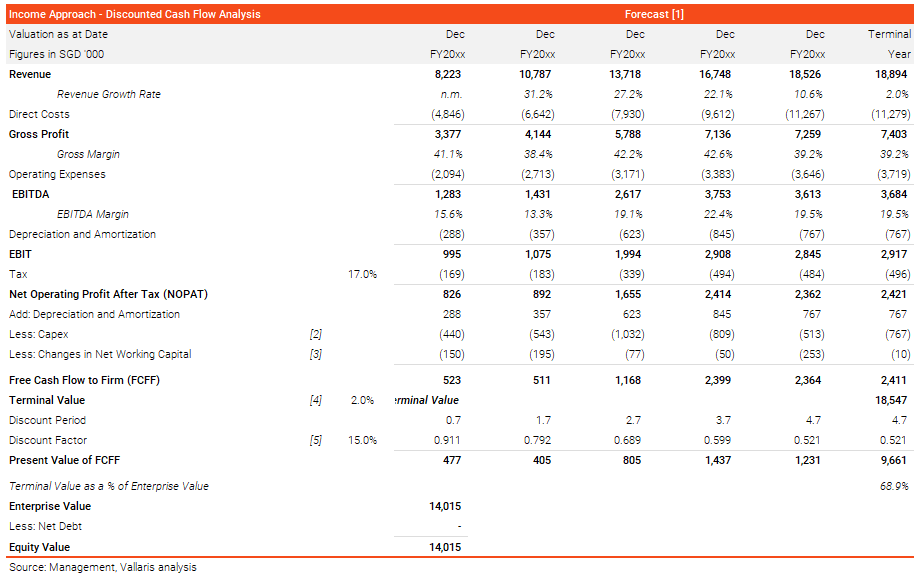
The DCF model requires more detailed attention to build compared to the three-statement model. It requires more estimates and assumptions. The value conclusion from a DCF model is dependent on the reasonableness of the applied estimates and assumptions. For example, aggressive estimates and assumptions would result in a high valuation as compared to conservative approach. Various scenarios can be analysed by performing sensitivity analysis to derive value.
Mergers & Acquisitions Model (M&A)
An M&A financial model analyzes the financial profile of two combining businesses. The objective is to model synergies created by the merger or acquisition. The M&A model also determines if the purchaser’s earnings per share (“EPS”) is likely to increase or decrease as a result. An increase is known as EPS accretion whilst a decrease is known as EPS dilution. Capital markets reflect favourably to deals that increase value for the purchaser.
Initial Public Offering (IPO) Model
An IPO model is created when a business wants to know the price of its shares before it sells its shares to the public for the first time. A valuer will undertake one or more business valuation methods to triangulate what the think is a reasonable price an investor will pay for the business.
Leveraged Buyout (LBO) Model
A LBO involves the acquisition of a target using significant amounts of debt. The assets of the target and purchaser are used as collateral for the loan. The aim of an LBO is to use cheaper debt to get access to higher earnings as result of buying the target.
A LBO model has a complex debt schedule model to evaluate how cash inflows from operation is to be paid to different types of capital providers. The LBO model is one of the most advanced models which is highly detailed and challenging to build. If there are many layers of financing, the LBO financial model may require circular references and cash flow waterfalls to analyze how to achieve the highest possible risk-adjusted internal rate of return.
There are more than ten types of financial models used across different industries. Each business’ needs are different. Hence it is important to understand a financial modelling engagement’s objective clearly so that that the model can adequately answer the questions asked by business leaders. There is no one-size-fit-all approach in financial modelling.
The financial model describes, analyses and projects a business or investment’s performance. Its objective is to virtually build out a business’ financial framework. Once the key drivers are identified as labelled as parameters, analysts are able to input different input assumptions that may change the outputs. We test inputs to analyse the impact they may have on a business or investment. These includes changes in unit selling prices and quantities, growth rates, product mix, variable and fixed costs, operating margins, funding structure and investor expectations.
As we have illustrated above, different financial models exist. One must know which is best suited for the purpose at hand and type of future decisions that is to be evaluated. Once it is determined what the model is being used for, a business can determine the proper design and functionality of that model to produce the needed results.
A financial model is a fundamental tool to assess and understand business risks in order to make strategic decisions. It is important to keep in mind that model building is not a repeated process, so do not expect to build the model quickly without any attention to the difference in application. Models are typically prone to errors. An effective model needs to be flexible and robust to explain the financial impact. However, it also needs to be user-friendly so that management can navigate the model easily with little training.
So, what are some of the best practices in creating a financial model using a spreadsheet? We get that question from time to time. A well-built model is simply a model that solves business problems. Here are some of the thought processes to help you construct a financial model:
exhibit 5: financial modelling best practices

Frame the business problem
Understand what the business goals and problems that you intend solve using the model. Identifying what’s important helps a financial modeler to design a bespoke model that achieves these objectives.
Simplicity
What are the minimum inputs and outputs required? Work hard to simplify the model to an elegant minimum that is be able to produce desired outcomes. The more assumptions the model needs, the more complex the model will be. So, try to keep the model as simple as possible!

Plan the layout
Planning the structure and layout of the model allow you to understand Step 2. This step gives you an overview of model structure and the drivers of your business. The model structure ultimately needs to contain these three components: (1) inputs, (2) calculations, and (3) outputs. It is important to clearly define and separate them.
Inputs are usually only entered once so it should be clarified beforehand. While the processing of inputs must be transparent and broken down into steps that are user friendly. Not only does it help a reader to understand the abstraction more easily, simplicity also speeds up the checking of logic accuracy and errors present in the model. The output should provide the information that users want to get in a glance, quick access and easy to understand. These three core elements are the essence of model planning.
Build your model
Use a spreadsheet software to build your model. A good model is structured so that each data is only entered once in the input sheet. Consider using different functions available in to protect data in different cells in case the user accidentally deletes parts of the model that does not require user input. It’ll be incredibly troublesome to rebuild from scratch! “One tip is to use ‘lock cell’, ‘conditional formatting’ or ‘data validation’ to protect data integrity.
Test
Congratulations! You have made it to the last step of building up a financial model. However, do not let your guard down. This is the most important step as it determines if your model will work well and completely functional for the purpose. Run stress test by using some dummy data inputs for all possible scenarios. For instance, if your business runs out of cash and the model still works. If it does and all other scenarios also do, congratulation you have a good model.
A well build model communicates complex financial analysis and numerical simulations powerfully by visualizing what’s important. Not all businesses desire financial models that are both robust and realistic. While large and realistic models are comprehensive, they can be too complex which makes them harder to build and use. On the other hand, small and robust models are easier to build and understand but they offer a lower degree of precision and flexibility. It is a trade-off that businesses have to make to balance resolution, flexibility and cost. If management requires highly realistic models to make strategic decisions, then more complex models are required. Otherwise, simple models may suffice.
Raymond Panko’s spreadsheet development error experiments found that up to 86% of spreadsheets have some form of error[1]. Given the diversity complexity of financial models, the chance of error, whether immaterial or catastrophic, is high.
A model audit’s purpose is to eliminate spreadsheet error. A model audit is also called a model review. This is to avoid confusion with financial audits.
A model audit seeks to ensure that coded and linked formulas and parameters are accurate and reliable. While we normally do check for errors, the scope of work for a financial model auditor is more than that. For example, a model auditor may also be asked to verify that the financial model complies with the prescribed guidelines. This may be specified in either a request for proposal’s bid advisory scope of work in a tender, procedural directions prescribed by a judge in an economic damages’ assignment, or by financial reporting standards.
Complex financial models tend to have more formulae and logic in place which give rises to possibility of errors within the models. However, the purpose of a model audit is not to opine on the elegance of a model’s design, but to confirm that its construction is consistent with the reference documents it is supposed to abstract as well as modelling best practices. This audit confirmation provides users of the model confidence that they may rely on the model’s outputs to make strategic decisions.
A formal model audit is performed to give clients and its stakeholders explicit and straightforward assurance that the financial model is free from material errors. Under a formal model audit, the entire model is to be checked thoroughly under high degree of scrutiny. This is usually the case when the model is to be submitted for a bid or deal completion bid advisory. After the audit, a financial audit report is generated to provide a detailed list of errors for the modeler to resolve prior to certifying that the financial model is free from material errors and can be relied on.
Financial modelling & audit is requested when businesses want to ensure that they can rely of their financial models for the following the following (non-exhaustive list):
Rules and regulation
Accounting rules and business regulations applicable to the business operation are fully incorporated into the model.
Formula and logic
Tests are to be performed to identify and remediate logic and formula errors. These includes formulas that do not comply with specifications, wrongly linked cells, circularities, logic errors, inconsistencies, hard coded cells, etc.
Data entry
Data fields and accompanying documentation is created to facilitate ease of use, prevent/alert a user to unacceptable inputs, suggest corrections automatically and minimize user errors.
At VALLARIS, we specialise in developing and reviewing financial models. These include models intended for a range of purposes e.g. tender, plan for growth, or to meet statutory reporting requirements. Our financial model provide for scenario planning and stress testing.
Positioning your high stakes project right is crucial to your success as a leader.
Request a meeting with VALLARIS.
References
[1] http://panko.com/ssr/DevelopmentExperiments.html